Search Results
Showing Results for insulin infusion systems
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a life-threatening infection caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2).1 Diabetes mellitus is one of the most frequent comorbidities, related to hospitalization due to SARS-CoV-2 infection, as well as a risk factor for disease severity, ...
The prevalence of diabetes during pregnancy is rapidly increasing. In the USA alone, an estimated 1–2% of pregnant women have type 1 diabetes (T1D) or type 2 diabetes (T2D), and an additional 6–9% develop gestational diabetes.1 From 2000 to 2010, the prevalence of gestational ...

Despite the increasing body of knowledge of treatment strategies for diabetes, many patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) are still in a persistent state of poor glycaemia.1,2 In clinical practice, achieving optimal glycaemic targets is challenging; the reasons are ...

Recent advances in technology have changed the landscape for managing diabetes treatment. Thanks to innovations such as connected insulin pens, sensor-augmented pump systems, automated insulin delivery, integrated mobile applications and continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems, people with diabetes now have ...

Automated insulin delivery (AID) systems play an important role in the management of type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) by helping users achieve the recommended glucose targets while reducing the episodes of hypoglycemia.1 First-generation AID systems, including MiniMed™ 630G (Medtronic, Dublin, ...

The World Health Organization (WHO) defines older adults as people aged 65 years or older.1 Today, older adults with diabetes mellitus (DM) are a growing population, with 33% of older adults meeting the criteria for DM.2 The risk of DM-related complications is ...

Diabetes is one of the most common co-morbidities associated with hospitalizations for SARS-CoV-2 infection, with recent estimates of diabetes prevalence ranging from 33.8%1 to 58.0%2 among hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in the USA. Hyperglycemia during the first hours after cardiac arrest is ...

The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has spread rapidly to become a global health threat. The disease is caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2), a novel β-coronavirus that belongs to a family of enveloped RNA viruses, the coronaviruses.1 While ...

Despite significant advances in technologies for the management of patients with type 1 diabetes (T1D), outcomes remain suboptimal across all age groups.1 Achieving glycemic control in patients with T1D requires precise and accurate methods of delivering insulin and monitoring ...

As technology has advanced over the last decade, so have the treatment options for patients with type 1 diabetes (T1D). The goal of these technological advances is improved regulation of glucose levels to more closely resemble glucose metabolism in patients ...

Various prandial insulins, including regular human insulin, aspart, glulisine, lispro and fast-acting insulin aspart (FIAsp), are used as part of basal plus, basal bolus, or prandial alone regimens. Some prandial insulins, also known as short-acting insulins, can also be used ...

About The American Association of Diabetes Educators The American Association of Diabetes Educators (AADE) is an interdisciplinary professional membership organization dedicated to improving prediabetes, diabetes, and cardiometabolic care through innovative education, management, and support. With more than 14,000 professional members including ...

Given the global nature of the diabetes epidemic,1 this condition is of public health importance in Sweden.2 National prevalence in Sweden is approximately 7.0%, based on a recent estimate,1 and approximately 90% of cases are type 2 diabetes (T2D).1,3 This prevalence ...
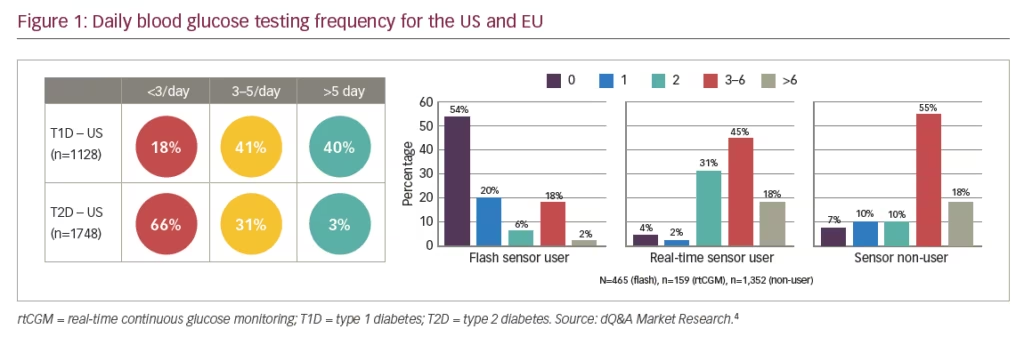
Self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) levels was the standard of care for achieving tight glycaemic control in patients with diabetes for several decades. Systems for continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) were introduced around 15 years ago and are employed by an increasing ...

Unmet needs for people with T2DM using intensive insulin Despite advances in diabetes management, many people with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) fail to achieve optimal glycaemic control, as demonstrated in a 2016–2017 audit of England and Wales, in which ...

Intensive insulin therapy is recommended for the management of type 1 diabetes (T1D),1 and has been shown to be an effective and beneficial treatment modality for many individuals with type 2 diabetes (T2D).2,3 During the past decade, we have seen ...
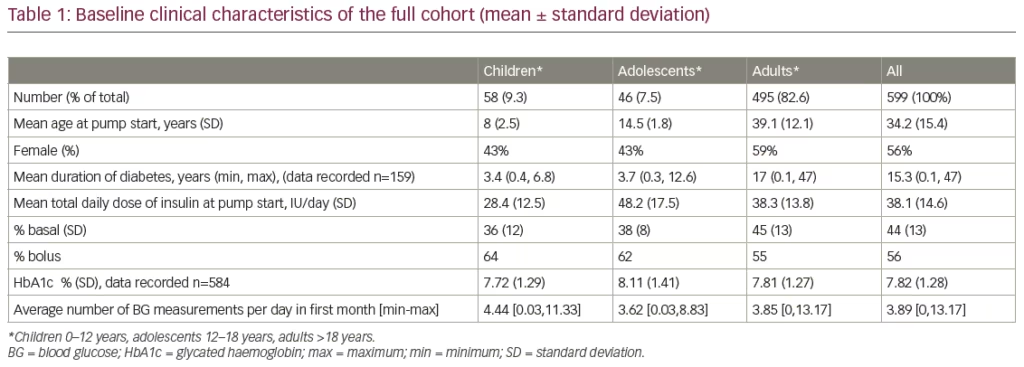
An effective basal-bolus regimen is the gold standard in type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) management as it most closely resembles physiological beta-cell pancreatic insulin secretion. Multiple daily injections (MDI) are commonly used to deliver insulin; however, where these fail to ...
Latest articles videos and clinical updates - straight to your inbox
Log into your Touch Account
Earn and track your CME credits on the go, save articles for later, and follow the latest congress coverage.
Register now for FREE Access
Register for free to hear about the latest expert-led education, peer-reviewed articles, conference highlights, and innovative CME activities.
Sign up with an Email
Or use a Social Account.
This Functionality is for
Members Only
Explore the latest in medical education and stay current in your field. Create a free account to track your learning.

