Search Results
Showing Results for regulatory T cells
Hepatic steatosis is the liver manifestation of metabolic syndrome and a common cause of chronic liver disease. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) diagnosis relies on the presence of hepatic steatosis, defined as >5% fat accumulation in the liver, as observed ...
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) is a ubiquitous, multifunctional, 766-amino acid, type 2 transmembrane glycoprotein, which participates in the regulation of metabolic functions, immune and inflammatory responses, cancer growth and cell adhesion.1 It has two forms: the first is a membrane-bound form, which ...

Obesity defined as abnormal or excessive fat accumulation that presents a risk to health, is a chronic disease linked to metabolic co-morbidities, such as type 2 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease, a reduced life expectancy, economic burden and reduced quality of ...

There has been an exponential increase in the global prevalence of obesity over the past few decades because of adverse lifestyle choices, such as physical inactivity and overconsumption of macronutrients. The obesity pandemic has contributed to more than 50 different disorders ...
Type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) is an autoimmune disease secondary to the destruction of the insulin-producing β cells of the islets of the pancreas. Environmental factors presumably trigger the disease in genetically susceptible individuals, leading to a lifetime dependency on exogenous ...

Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) encompasses a spectrum of fatty liver diseases, including non-alcoholic fatty liver (NAFL) and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).1 NAFLD is associated with metabolic disorders, including obesity, hypertension, dyslipidaemia, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), hypothyroidism and metabolic syndrome.2 ...

Nutrient-stimulated gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP) (known as either gastric inhibitory polypeptide or glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide) or glucagon-like peptide (GLP-1), are secreted by K and L cells, respectively, in the upper segment of the small intestine and throughout the intestine. For ...

Obesity – a chronic, relapsing, progressive disease that is defined by a body mass index (BMI) of ≥27.5 kg/m2 in Asian populations and ≥30.0 kg/m2 in all other populations – is an epidemic that has spread across the world.1 Recent data from ...

Acromegaly is a chronic, progressive disease characterized by an excess secretion of growth hormone, and consequently, increased circulating insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) levels. These patients typically exhibit acral and soft tissue overgrowth, headache, arthritis and visual disturbances. Impaired glucose tolerance ...
Immune checkpoints are small molecules that are present on the cell surface of T lymphocytes to regulate the immune response. While some of these molecules enhance the stimulatory signals, others boost the inhibitory signals to blunt the activity of T ...

World Health Organization statistics rank tuberculosis (TB) amongst the top 10 communicable diseases in the world, and it remains one of the biggest killers of mankind.1 TB is known to cause both mortality and morbidity. Pulmonary TB is the primary manifestation, ...

The use of immunotherapy in the treatment of cancer has been revolutionary, opening a new era in the fight against cancer. The principle of immunotherapy involves using pharmacotherapy to harness the power of the body’s own immune system to ...

The International Diabetes Federation (IDF) estimates that 463 million people worldwide suffer from diabetes, 90% of whom have type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), and expects the total healthcare expenditure on diabetes to reach US$ 845 billion by 2045 from US$ 760 billion in 2019.1 People with ...

The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has spread rapidly to become a global health threat. The disease is caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2), a novel β-coronavirus that belongs to a family of enveloped RNA viruses, the coronaviruses.1 While ...

The diabetes pandemic affects millions of individuals throughout the world; the prevalence, especially of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), is increasing and shows no signs of abating. According to the International Diabetes Federation, the number of adults living with diabetes (...
The armamentarium of anticancer drugs available to an oncologist has grown rapidly over the past few decades. The use of cancer immunotherapy and targeted therapy has become more popular in the last few years. It has also become increasingly clear ...

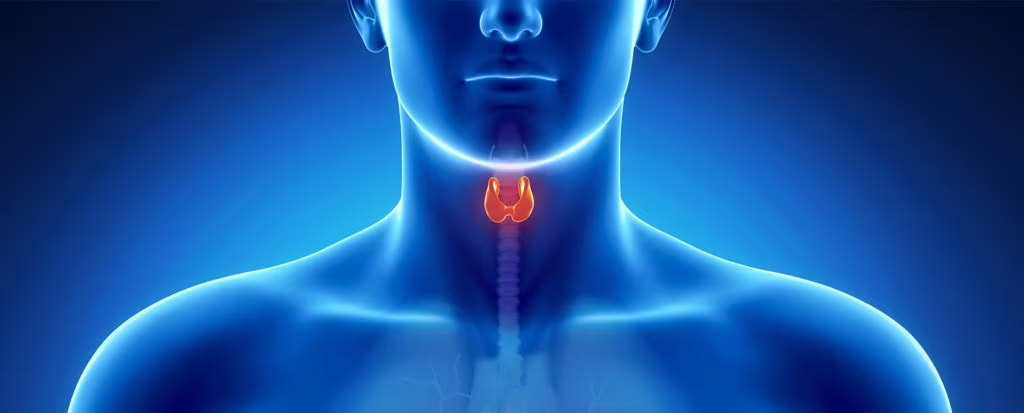
Thyroid nodules are common and frequently benign, with approximately 5–10% being malignant.1 Current diagnostic evaluation of thyroid nodules should include a multidisciplinary approach, integrating clinical, sonographic, cytologic, and molecular analysis. While fine-needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy and cytologic examination have emerged as ...

In the adult male, hypogonadism is usually defined by the failure of the testis to produce physiological concentrations of testosterone and/or a normal number of spermatozoa.1 When due to abnormalities of the hypothalamic-pituitary axis, the condition is referred to ...
Latest articles videos and clinical updates - straight to your inbox
Log into your Touch Account
Earn and track your CME credits on the go, save articles for later, and follow the latest congress coverage.
Register now for FREE Access
Register for free to hear about the latest expert-led education, peer-reviewed articles, conference highlights, and innovative CME activities.
Sign up with an Email
Or use a Social Account.
This Functionality is for
Members Only
Explore the latest in medical education and stay current in your field. Create a free account to track your learning.

